Mmol/L to mg/dl Formula The following formula is used to convert mmol/L to mg/dl mg/dl = 18 * mmol/l Where mg/dl is the milligrams per deciliter mmol/l is the millimoles per liter How do you convert mmol/L to mg/dL?60 150 mg/dL mmol/L 2 Click on the link to go to Equation page Warning Physicians and Healthcare Professionals are responsible to employ good clinical judgement in selecting and interpreting Clinical data (history, physical, signs, symptoms, maneuvers, labs, tests, parameters, inputs, outputs, etc), and to verify all processingCreatinine Unit Conversion between mg/dL and µmol/L Note Fill in one box to get results in the other box by clicking "Calculate" button Data should be separated in coma (,), space (

Updates Of Diabetes Management By Dr Selim
180 mg/dl to mmol/l
180 mg/dl to mmol/l-This is a free online tool by EverydayCalculationcom to convert blood alcohol level values from milligrams per liter to millimoles per liter and viceversaQuest'ultima unità di misura è quella adottata dal SI e come tale rappresenta lo standard di riferimento a livello internazionale



Calculate In Mg Dl The University Of Edinburgh
Mg/dl to Millimole Per Liter The formula used to convert mg/dl to Millimole Per Liter is 1 Milligram Per Deciliter = Millimole Per Liter Measurement is one of the most fundamental concepts Note that we have Fahrenheit as the biggest unit for length while Per Degree Celsius is the smallest oneTo convert blood sugar (glucose, molar mass = g/mol) from mmol/L to mg/dl and vice versa, use the following conversion equation 1 mmol/L = 18 mg/dl0701 mg/dL Children Neonates premature 2591 μmol/L mg/dL Neonates full term 2175 μmol/L mg/dL 212 m 1537 μmol/L mg/dL 1< 3 y 2136 μmol/L mg/dL 3< 5 y 2742 μmol/L mg/dL 5< 7 y 2852 μmol/L 0359 mg/dL 7< 9 y 3553 μmol/L mg/dL 9< 11 y 3465 μmol/L mg/dL
mg/dl naar mmol/l mg/dl = mmol/l delen door 0,0555 Bijvoorbeeld 3,3 / 0,0555 = 59,46 ≈ 60411‐5 mmol/L 74‐106 mg/dL 60‐90 years 456‐638 mmol/L ‐115 mg/dL > 90 years 416‐672 mmol/L 75‐121 mg/dL Children 333‐555 mmol/L 60‐100 mg/dL Neonates (1 day) 222‐333 mmol/L 40‐60 mg/dL Neonates (> 1 day) 278‐444 mmol/L 50‐80 mg/dL To convert from mg/dL to mmol/L, we divide the unit mg/dL value by 18 or multiply it by 055 (since 1/18=055) Thus, for example, a blood glucose of 900mg/dL is equivalent to a blood glucose of 50 mmol/L, since 900/18=50 So, again, both values measure blood glucose the exact same way, just in different measurements
Mg/dl 95 100 110 1 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 0 210 2 230 240 250 mmol/L 53 56 61 67 72 78 94 100 105 111 117 122 128 133 139Milligram per deciliter, the unit used in medicine to measure the concentration of substances in the blood 1 mg/dl equals 001 grams per liter (g/L)1 mmol/L equals approximately 18 mg/dL Therefore, in order to convert from mmol/L to mg/dL, the blood glucose value needs to be multiplied by 1801 1 mg/dL equals approximately 0055 mmol/L Therefore, in order to convert from mg/dL to mmol/L, the glucose value needs to be multiplied by
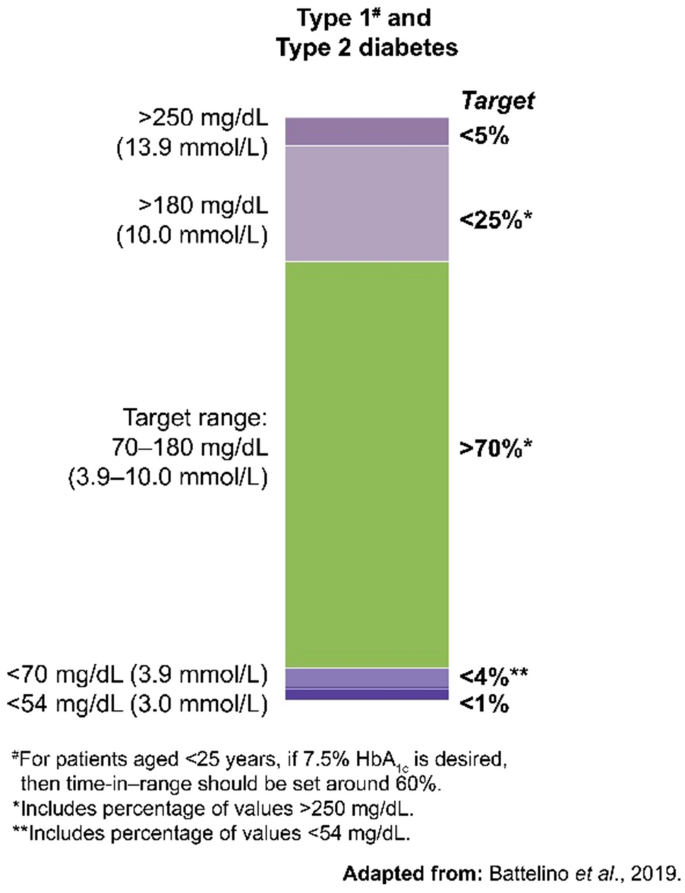



Individualizing Time In Range Goals In Management Of Diabetes Mellitus And Role Of Insulin Clinical Insights From A Multinational Panel Springerlink




Hba1c Chart Diabetestalk Net
Diabete >126 > 70 Questi valori non sono costanti nel tempo, perché dipendono dall'assunzione di cibi post prandiale, il valore è compreso tra mg/dl durante il digiuno, il valore può scendere a 6070 mg/dl, se il valore rilevato è compreso tra , si ha un'alterata glicemia a digiuno, se il valore è superiore a 126 mg/dl At bedtime From 90 to 150 mg/dL (50 to mmol/L) for adults If an individual has type 2 diabetes, levels should be the following 4 Before meals From 70 to 130 mg/dL (39 to 72 mmol/L) for adults After meals (1 to 2 hours after eating) Less than 180 mg/dL (100 mmol/L) for In most of the world, except for the United States, blood glucose test results are reported as mmol/L In the United States, milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) is used To convert to mmol/L from mg/dL, divide mg/dL by 18 Example 180 mg/dL ÷ 18 = 10 mmol/L




Time In Range Centered Diabetes Care Abstract Europe Pmc
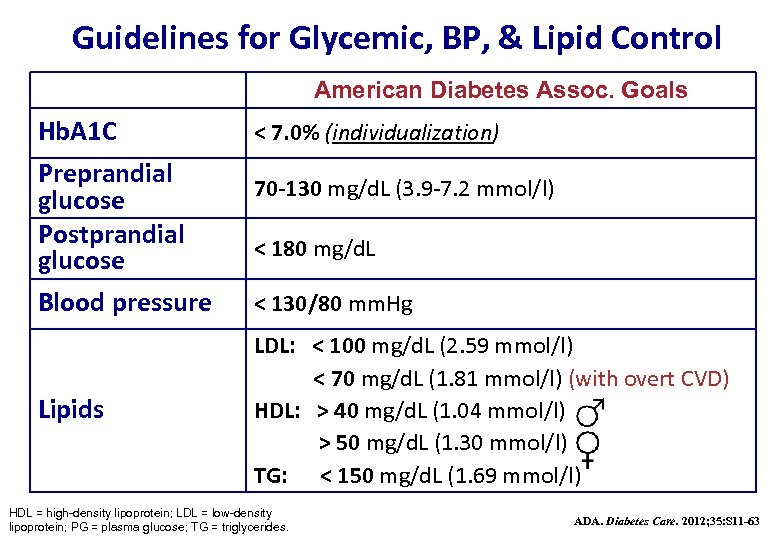



Diabetes Management In The Outpatient Setting Diagnostic
›› Quick conversion chart of mg/dL to g/L 1 mg/dL to g/L = 001 g/L For example, if your reading is 12 mmol/L, you multiply 12 mmol/L by 18, which equals 216, and change the units to mg/dL 216 mg/dLPeople from outside the US may find this table convenient for converting US blood glucose values which are given in mg/dl into values generated by their blood glucose meters, which are generated in mmol/LThe international Formula to calculate mg/dl from mmol/l mg/dl = 18 × mmol/l Can I change the units given by my blood glucose meter?




Hypercholesterolaemia Practical Information For Non Specialists Abstract Europe Pmc
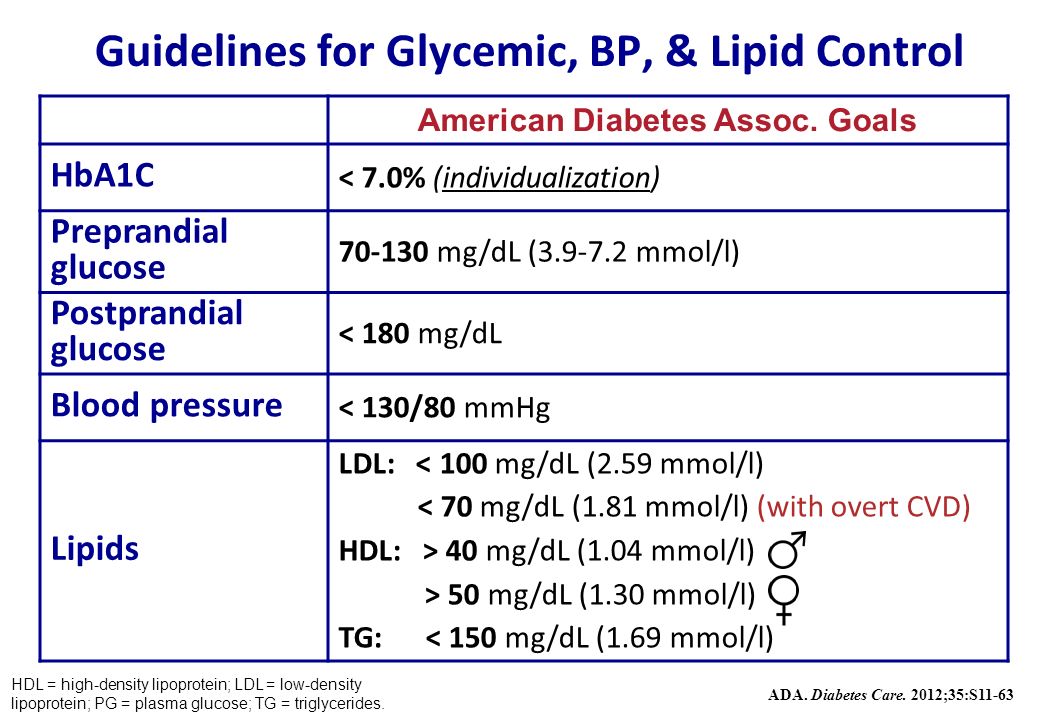



Diabetes Management In The Outpatient Setting Ppt Video Online Download
180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) 72 180 mg/dL (4 10 mmol/L) A fluctuation of 108 mg/dL (6 mmol/L) over the course of the day The example above does not reflect your individual situation;In order to convert milligrams per deciliter multiply the total amount of mmol/L by 18 This will convert the value into mg/dLFor the majority of healthy individuals, a normal blood sugar range is Fasting range between 70 and 100 mg/dL (39 to 56 mmol/L ) Optimal nonfasting range before a meal is less than 100 mg/dL (55 mmol/L ) When operating normally the body restores blood sugar levels to a range of to 110 mg/dL (44 to 61 mmol/L) within two hours after eating




Strict Glycemic Targets Need Not Be So Strict A More Permissive Glycemic Range For Critically Ill Children American Academy Of Pediatrics




Blood Sugar Glucose Conversion Chart Mmol L To Mg Dl Disabled World
Based on observations that mean renal threshold for glucose is approximately 40 mg/dL (22 mmol/L) higher in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 18) than the commonly reported values of 180 to 0 mg/dL (10–11 mmol/L) in healthy individuals 19) and using a mean GFR of 100 mL/min, calculations suggest that elevated renal threshold for glucose leads to anThis can depend on which blood glucose meter you haveThe abbreviation for µmol/L and mg/dL is micromole per liter and milligram per deciliter respectively 1 µmol/L is times smaller than a mg/dL To measure, units of measurement are needed and converting such units is an important task as well unitsconverterscom is an online conversion tool to convert all types of measurement units including µmol/L to mg/dL conversion




Lipoprotein A Lowering By 50 Mg Dl 105 Nmol L May Be Needed To Reduce Cardiovascular Disease In Secondary Prevention Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis And Vascular Biology




Clinical Targets For Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation Recommendations From The International Consensus On Time In Range Diabetes Care
OMRÄKNINGSTABELLLER mmol/L, mg/dL Omräkning mg/dL till mmol/L (mg/dL x 0,0555 = mmol/L) Omräkning mmol/L till mg/dL (mmol/L x 18,016 = mg/dL) Gilla GlucoMen på Facebook wwwareonu shopmenarinidiagnosticsse mmol/L mg/dL 2 ~ 36 3 ~ 54 4 ~ 72 5 ~ 90 6 ~ 108 7 ~ 126 8 ~ 144 9 ~ 162 10 ~ 180 11 ~ 198 12 ~ 216 13 ~ 234 14 ~ 252 15 ~ 270 16 ~ 2 A level of 70 mg/dL or less is now recommended for persons with existing heart disease HDL's Good Fats and promote opening up of the arteries > 50 mg/dL (≈ 13 mmol/L) man or >60 mg/dL (≈ 16 mmol/L) in a woman a reduced risk of atherosclerosis >75 mg/dL (≈ 2 mmol/L) man or woman is associated with a very low risk of atherosclerosis105 mg/dL mmol/L 2 Click on the link to go to Equation page Warning Physicians and Healthcare Professionals are responsible to employ good clinical judgement in selecting and interpreting Clinical data (history, physical, signs, symptoms, maneuvers, labs, tests, parameters, inputs, outputs, etc), and to verify all processing (data




Blood Sugar Level Wikipedia




Assessment Of Glycemic Control Protocol Star Through Compliance Anal Mder
70 to 100 mg/dl (40 to 54 mmol/l) Postprandial blood sugar (2 hours after a meal) Less than or equal to 140 mg/dl (78 mmol/l) Random blood sugar (irrespective of your meal time) Levels vary depending on what and when was the last time Should be less than 140 mg/dl (78 mmol/l) if not taken soon after a mealMg/dL mmol/L Decimals 1 Decimals 2 Decimals 3 Decimals 4 Decimals 5 Decimals 6 Decimals 7 Decimals 8 Decimals 9 Decimals 10 Decimals 11 Decimals 12 Decimals 13 Decimals No Decimal This calculator converts cholesterol units form the popularly used mg/dL to the SI units mmol/L It works for total serum cholesterol, HighDensity Lipoproteins (HDL), LowDensity Lipoproteins (LDL), and triglyceridesConverting cholesterol levels measurement units by yourself can be overwhelming, so read on to understand how our cholesterol calculator works and what




Mmol L To Mg Dl Conversion Share Fudiabetes
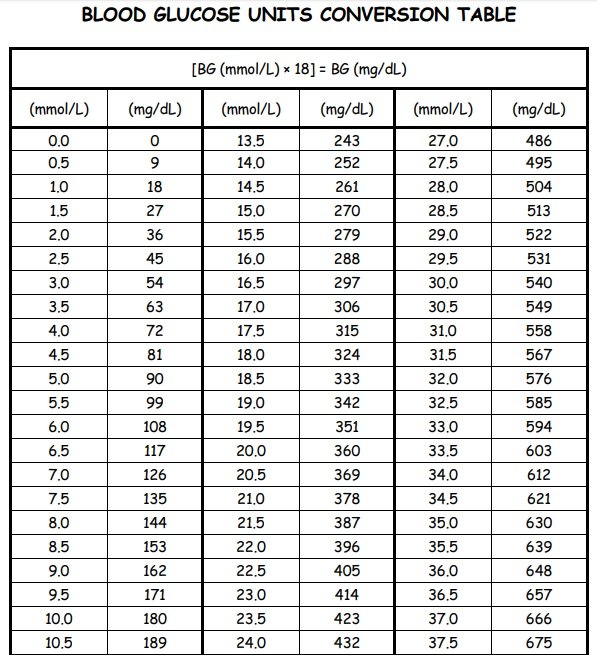



Free Printable Blood Sugar Chart Template Excel Word Pdf Best Collections
How do you find mg/dL value to mmol/L chart?1 mg/dL value equivalent in mmol/L = Please note you need to seek your doctor advice on any medical issues concerning you for professional advices Below is1 kilogram/cubic meter is equal to 100 mg/dL, or 1 g/L Note that rounding errors may occur, so always check the results Use this page to learn how to convert between milligrams/decilitre and grams/liter Type in your own numbers in the form to convert the units!
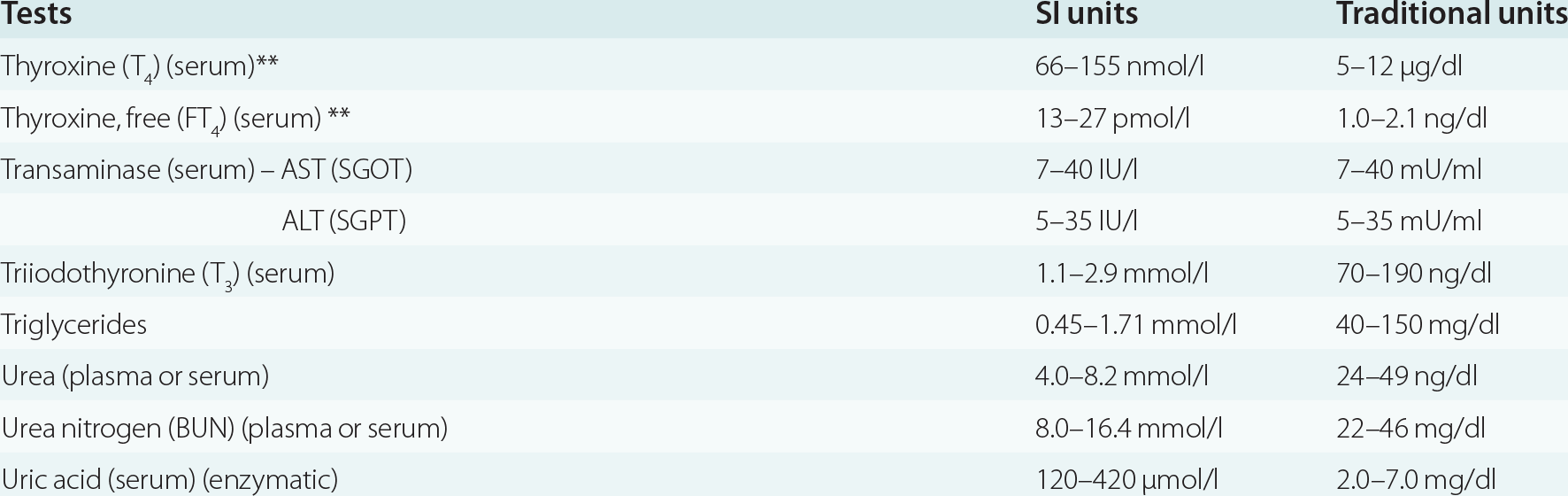



Clinical Laboratory Tests Reference Values Appendix B Case Studies In Neurological Infections Of Adults And Children




Diabetes Mmol L
I valori ematici di glucosio vengono espressi in milligrammi per decilitro (mg/dL) oppure in millimoli per litro (mmol/L);Milligrams per decilitre (mg/dl), used in the United States and Europe, measures the concentration of glucose as a ratio of weight to volume Millimoles per litre (mmol/l), used in the United Kingdom, measures the concentration of glucose as a ratio of molecules to volume 80–130 mg/dl (44–72 mmol/L) 1 to 2 hours after meals Normal for person without diabetes Less than 140 mg/dl (78 mmol/L) Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes Less than 180 mg/dl (100 mmol/L)




Impact Of Glucose Management Team On Outcomes Of Hospitalizaron In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Admitted To The Medical Service Endocrine Practice



3
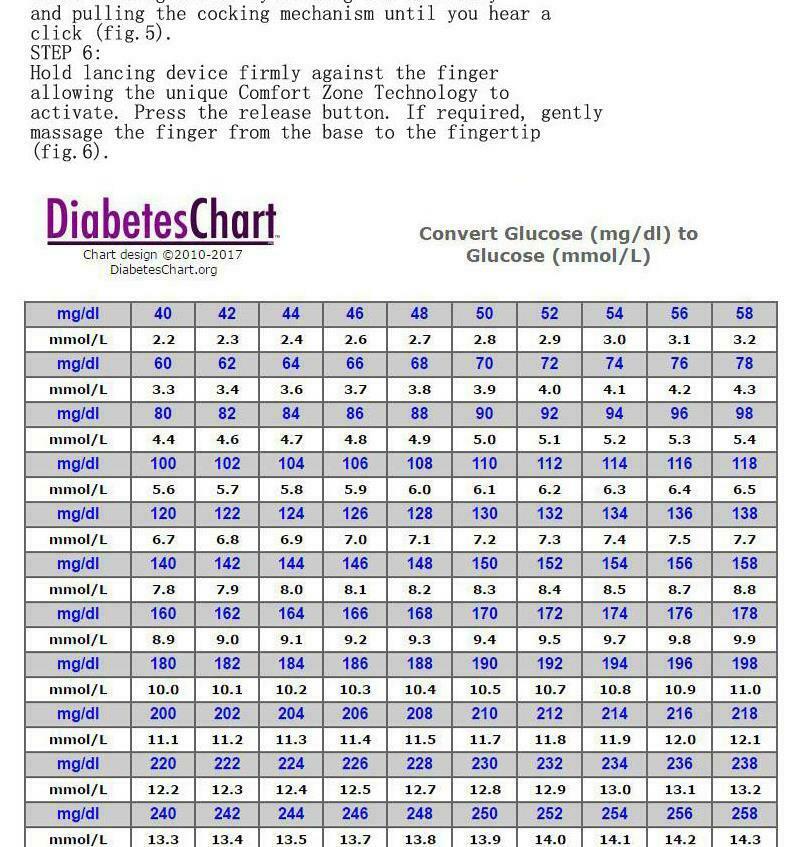
Glucose (mg/dl) to glucose (mmol/L) conversion chart Advertisement Chart design ©1018 DiabetesChartorg Convert Glucose (mg/dl) to Glucose (mmol/L) mg/dl 40 42 44Umgekehrt kann man den mmol/l Wert ganz einfach in mg/dl umrechnen, indem man den Wert mit 18,02 multipliziert Gesamtcholesterin 140 mg/dl Im Rechner wird folgende Umrechnungsformel genutzt 1 mmol/l = 18,02 mg/dl WieAnswer When you are converting between 1 cholesterol (LDLC) 1 mg/dL value equivalent in mmol/L = Please note you need to seek your doctor advice on any medical issues concerning you for professional advices



Discovery Ucl Ac Uk Id Eprint 1 1015 diabetes care accepted Pdf




Diabetes Mellitus Disorders Of Organ Systems Pharmacotherapy Principles And Practice Second Edition Chisholm Burns Pharmacotherapy 2nd Ed
Diabetics should regularly monitor their blood sugar to ensure they stay within the target range set for them by their doctorsYou can select a range within 70 to 180 mg/dL (39 to 100 mmol/L) Note The range must be at least 30 mg/dL (17 mmol/L) wide (eg 90 to 1 mg/dL (50 to 67 mmol/L)) in order to generate reports These additional parameters are used only by the Glucose Pattern Insights report and are saved to the ReaderOn average, normal glucose levels typically peak at 160 180 mg/dl (8 10 mmol/l) from 30 minutes to 1 hour after administration of the oral glucose dose, and should then return to fasting levels of 140 mg/dl (778 mmol/l) or less within a 2 to 3hour period"thank you for your help!




Management Of Blood Glucose In Icu Cancer Therapy Advisor




Conversion Of Blood Sugar Level Mmol L To Mg Dl Diabetestalk Net
Le perone al di fuori degli tati Uniti poono trovare queta tabella utile per convertire i valori tatuniteni di glucoio nel angue che ono dati in mg / dl in valori generati dai loro miuratori di glucoio nel angue, che ono generati in mmol / L 1 mg / dL = 1 / 1815 mmol / L mmol / L mg / dl mmol / L mg / dl mmol / L mg / dl 006 1 67 1 160 2 028 5 70 126 166 300 055 10 72 130 170Although the initial trials in Leuven produced enthusiasm and recommendations for intensive blood glucose control, the results of the NICESUGAR study have resulted in the more moderate recommendation to target a blood glucose concentration between 144 mg/dL and 180 mg/dL (810 mmol/L)Таблица перевода значений mg/dl в mmol/l в Америке используют другие меры измерения сахара в крови, эта таблица поможет вам сопоставить результаты в привычные единицы




Appendix I Glucose Conversion Between Mg Dl And Mmol L Mg Dl Mmol L Mg Dl Mmol L Mg Dl Mmol L Mg Dl Mmol L Insulin Hypoglycemia



Mg Dl To Mmol L Glucose Calculator
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be From 90 to 150 mg/dL (50 to mmol/L) for adults From 90 to 150 mg/dL (50 to mmol/L) for children, 13 to 19 years old From 100 to 180 mg/dL (55 to 100 mmol/L) for children, 6 to 12 years old Keeping this in consideration, is blood sugar of 94 high?When you purchase through links on this site, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you *** 18 mg/dL of blood glucose = 1 mmol/L of blood glucose Note that in Canada, there's a higher allowable reading for a normal fasting blood sugar level38 righe mg/dl x = mmol/l mmol/l x 1801 = mg/dl Note that this conversion rule refers only to glucose Other substances such as cholesterol and triglycerides must be coverted by other factors as they have other molar masses Look at the SI Unit Table and calculator for other substances than glucose




Lec 11 Perioperative Assessment For Diabetes For Mohs




Insulin Titration At Home Diabetes And Coronavirus Intolife
Conversor mg/dL ↔ mmol/L Calculadoras UCI SeleccionaUreaBUNSodioPotasioCalcioMagnesioFosfatoCloruroCreatininaBilirrubinaAcUricoColesterolTrigliceridosGlucosaLactato mg/dlmmol/Lµmol (Cr y Br) Resultado RPitarch ©© 14 Conversor mg/dL ↔ mmol/L Close 쉽게 정리하면 포도당의 분자량은 180gm/mol dL / L 만일 혈중레벨이 8 mmol/L 라면 8 x 180 x 100/1000 = 8 x 18 = 144 mg/dL (mg%) The blood glucose level may rise temporarily after meals, in nondiabetics up to 78 mmol/L (140 mg/dL) According to the American Diabetes Association, the blood glucose target range for diabetics should be 50 to 72 mmol/l (90 to 130 mg/dL) before meals, and less than 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) after meals




Conversion Mg Dl Mmol L




Glycaemic Variability In Diabetes Clinical And Therapeutic Implications The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology



1




Blood Glucose Targets For Patients On Basal Bolus Insulin Regimen Download Scientific Diagram




Mmol L To Mg Dl Conversion Share Fudiabetes




Blood Glucose Conversion Table Robot Robotics




Diabetes Mellitus Part 2




Normal Blood Sugar Values Molarity And Fluctuations




Can Urine Glucose Substitute For Fingerstick Glucose In




Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Dr Abha Gupta Professor Of




Convert Blood Glucose Mmol L To Mg Dl Rendering Of Mmol Clothe In Received Pronunciation
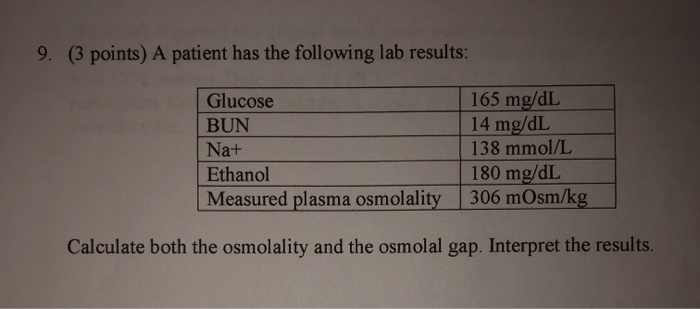



Solved 9 3 Points A Patient Has The Following Lab Resu Chegg Com



Calculate In Mg Dl The University Of Edinburgh




How To Convert Units From Mg Dl To Mmol L Youtube
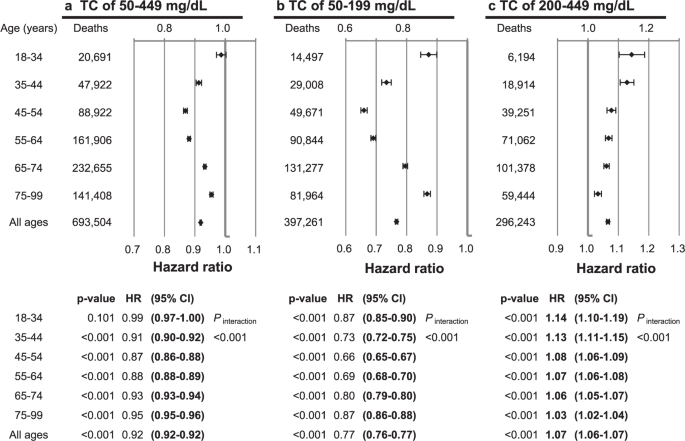



Total Cholesterol And All Cause Mortality By Sex And Age A Prospective Cohort Study Among 12 8 Million Adults Scientific Reports




Remissione Del Diabete Tipo 2 Terapia Medica Dr Monica Nannipieri Dipartimento Di Medicina Clinica E Sperimentale Universita Di Pisa Ppt Download




Updates Of Diabetes Management By Dr Selim




Blood Sugar Glucose Converter For Diabetes



1
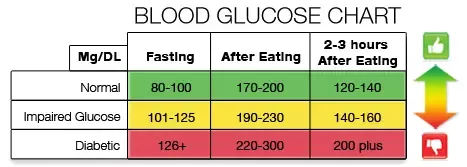



What Is A Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Level Quora




Convert The Following Si Units To Metric Units By Usi Chegg Com




Figure 11 Study Igbj Mean Glucose Concentrations Post Glucagon Dose Mmol L Mg Dl Clinical Review Report Glucagon Nasal Powder Baqsimi Ncbi Bookshelf




Continuous Glucose Monitoring Assessment Of Metabolic Control In East African Children And Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Pilot And Feasibility Study Mcclure Yauch Endocrinology Diabetes Amp Metabolism Wiley Online Library




What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level Diabetes Self Management



2




Lipoprotein A Lowering By 50 Mg Dl 105 Nmol L May Be Needed To Reduce Cardiovascular Disease In Secondary Prevention Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis And Vascular Biology




Global Risk Management In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus American Journal Of Cardiology




Glucose Conversion Chart Diabetestalk Net




1 Blood Glucose 1 Mg Dl 6 8 Mmol L On Two Repeated Measurements Normal Range For Blood Glucose Mg Dl Mmol L Boarderline Concentrations Ppt Download



Plos Medicine Clinical Outcomes In A Primary Level Non Communicable Disease Programme For Syrian Refugees And The Host Population In Jordan A Cohort Analysis Using Routine Data




Closing The Loop On Managing Youth With Type 1 Diabetes Children Are Not Just Small Adults Diabetes Care
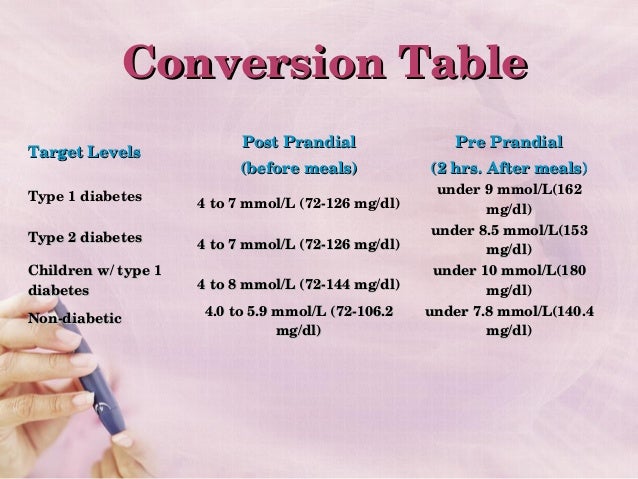



Diabetes Care Solution




Table 2 Proportion Of Patients With Predefined Aggregate Ukpds Clinical End Points Classified According To Whether They Had Low 140 Mg Dl 7 8 Mmol L Intermediate 140 To 180 Mg Dl 7 8 To 10 0 Mmol L Or High 180 Mg Dl 10 0 Mmol L Fpg
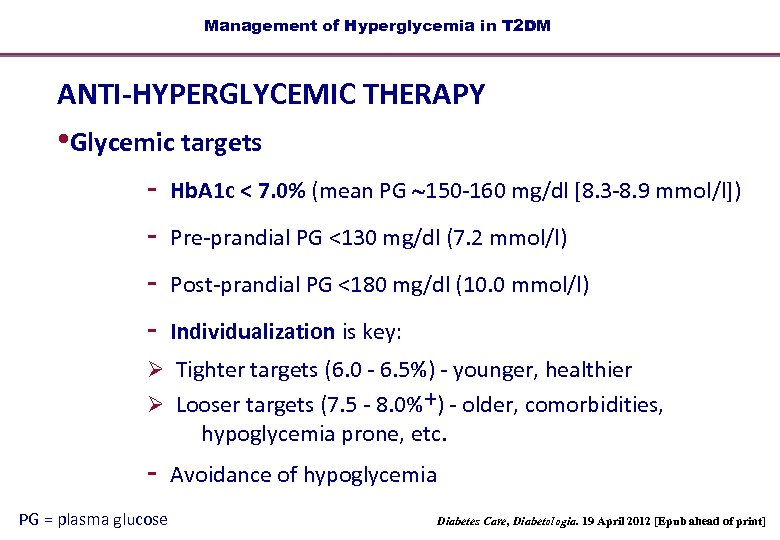



Diabetes Management In The Outpatient Setting Diagnostic




Glucose Mmol L Mg Dl Reference Ranges For All Adult Common Loon Download Table




Blood Sugar Level Wikipedia
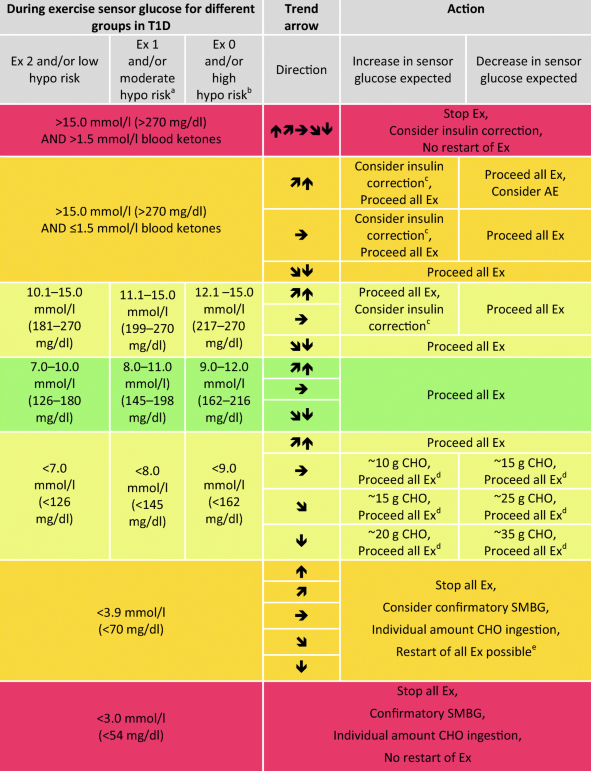



Table 2 Glucose Management For Exercise Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring Cgm And Intermittently Scanned Cgm Iscgm Systems In Type 1 Diabetes Position Statement Of The European Association For The Study Of




Sinocare Mmol L Or Mg Dl Are 2 Units Used In Different Facebook
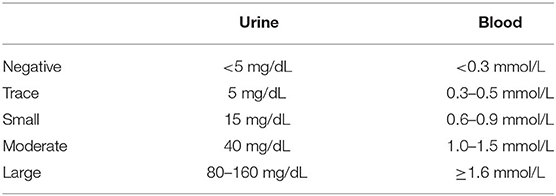



Frontiers Monitoring Of Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes Endocrinology




Doc Blutzuckerwerte Tabelle Peter Schachtschabel Academia Edu



2




Agp And Nutrition Analysing Postprandial Glucose Courses With Cgm Sciencedirect
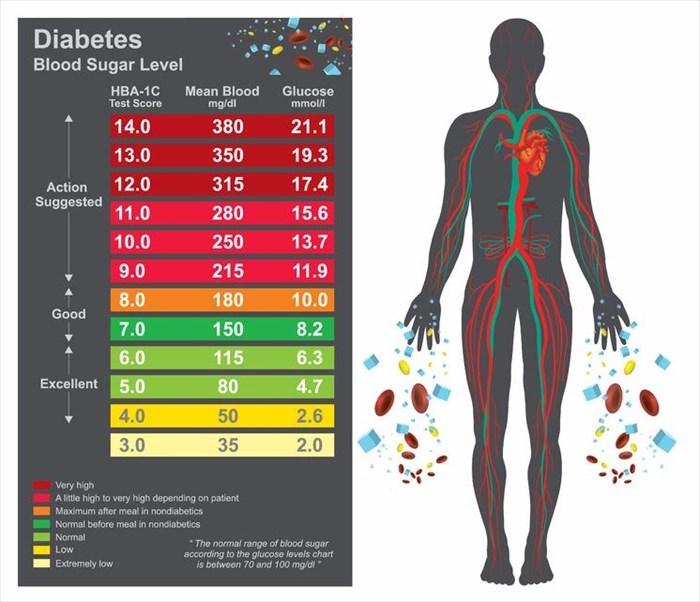



What Is Considered A Normal Blood Sugar Level




Mmol L To Mg Dl Conversion Share Fudiabetes




Blutzucker Umrechnungstabelle




Pin On Medicine




6 Glycemic Targets Standards Of Medical Care In Diabetes 21 Diabetes Care



Your Child Can Exercise Safely With T1d



Plos Medicine Clinical Outcomes In A Primary Level Non Communicable Disease Programme For Syrian Refugees And The Host Population In Jordan A Cohort Analysis Using Routine Data




Improved Time In Range And Glycemic Variability With Sotagliflozin In Combination With Insulin In Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Pooled Analysis Of 24 Week Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data From The Intandem Program




Answered Diabetes Control Chart Excellent Good Bartleby



Www Royalcollege Ca Rcsite Documents Credential Exams Clinical Lab Tests Reference Values E Pdf



Stretching The Range Will Not Solve The Problem Securecell Website



Sinocare 100pcs Accu Blood Glucose Test Strips For Diabetic Sugar Meter Codefree Ebay



About Pch




Comparison Of Second Generation Basal Insulin Analogs A Review Of The Evidence From Continuous Glucose Monitoring Diabetes Technology Therapeutics




Increased Time In Range And Fewer Missed Bolus Injections After Introduction Of A Smart Connected Insulin Pen Abstract Europe Pmc




Strict Glycemic Targets Need Not Be So Strict A More Permissive Glycemic Range For Critically Ill Children American Academy Of Pediatrics



Nursing Questions Bingo Card




Blood Glucose Conversion Tables
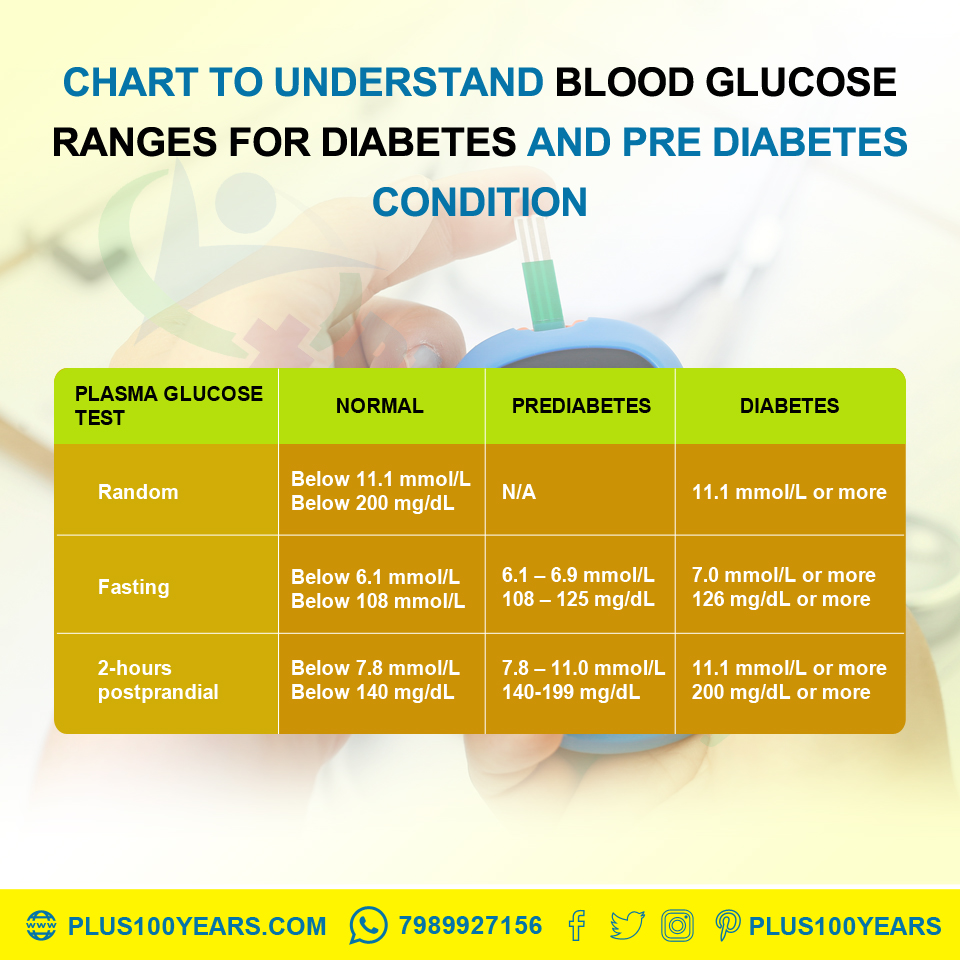



Know Blood Glucose Levels To Manage Diabetes Perfectly




Impact Of Glucose Management Team On Outcomes Of Hospitalizaron In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Admitted To The Medical Service Endocrine Practice




Solved 4 Convert The Glucose Result 255 Mg Dl To Mil Chegg Com




2 Current Management Of Diabetes Introduction To Primary Care A Course Of The Center Of Post Graduate Studies In Fm Po Box Riyadh Tel Ppt Download
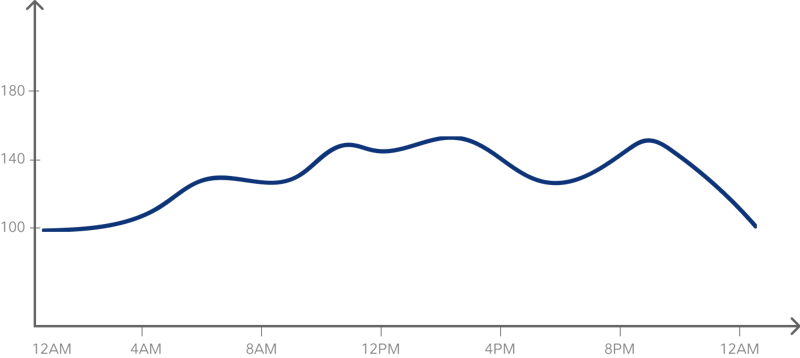



The Dawn Effect What We Know And What We Don T Diet Doctor




Control Concentrations Of Plasma Glucose Mg Dl Lactate Mmol L Download Table
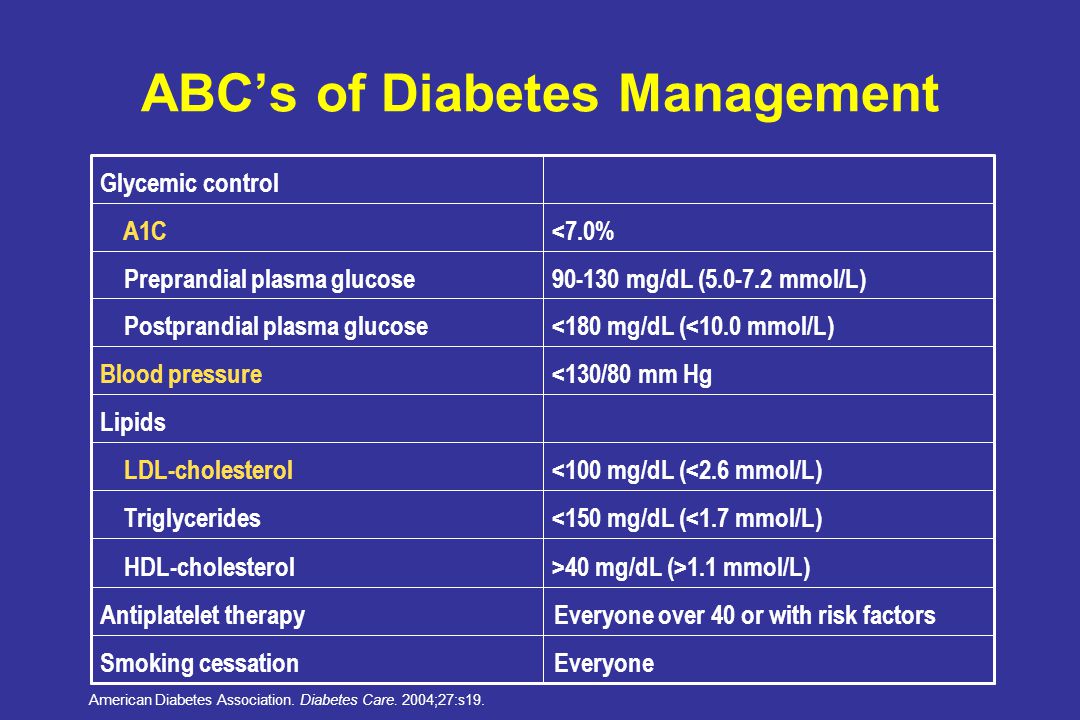



Current Advances In Diabetes Management Ppt Video Online Download



Educate Diabetes Mellitus



1




Following Glucose Guidelines Can Be Misleading Denise A Pancyrz Reverse My Diabetes




Lrinec Score For Necrotizing Fascitis Mnemonic Epomedicine




Managing Children And Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes During The Covid 19 Pandemic Covid 19 And Childhood Diabetes




Solved 11 The Concnetration Of The Following Solutes Wh Chegg Com
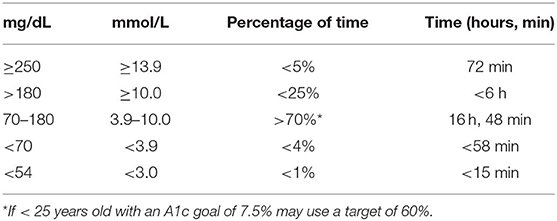



Frontiers Monitoring Of Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes Endocrinology




Continuous Glucose Monitoring Assessment Of Metabolic Control In East African Children And Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Pilot And Feasibility Study Mcclure Yauch Endocrinology Diabetes Amp Metabolism Wiley Online Library
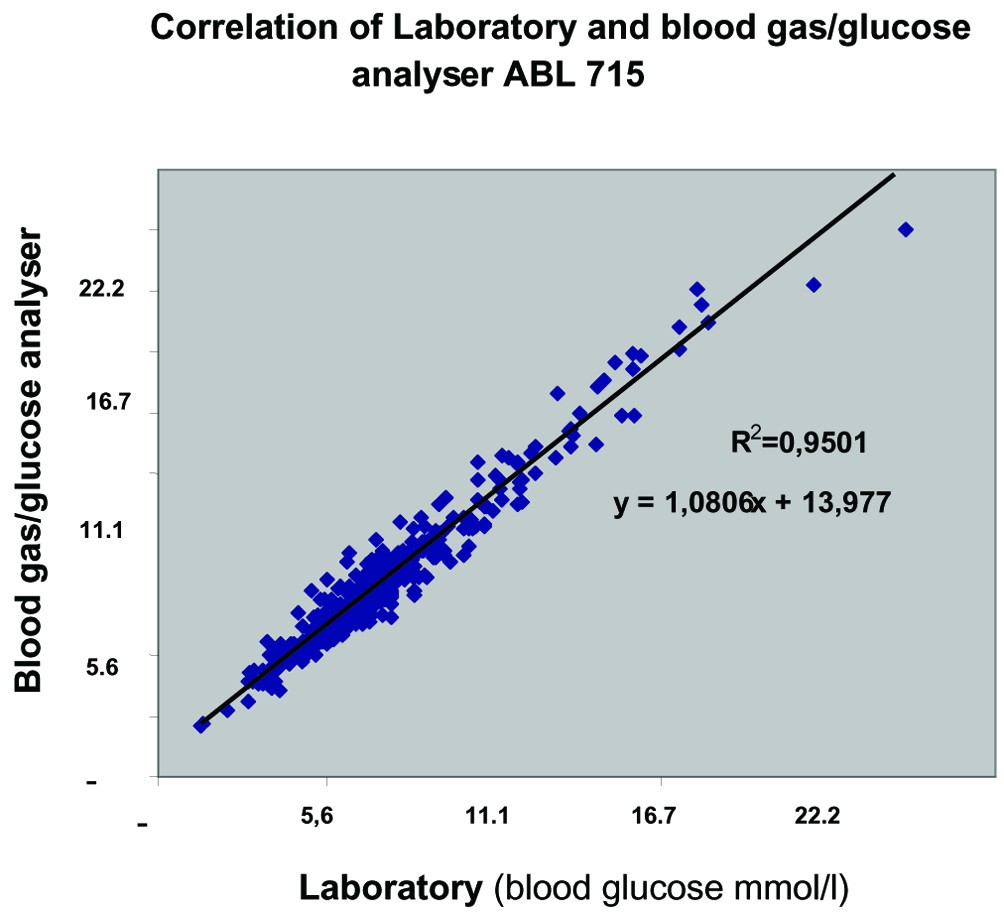



Accuracy And Feasibility Of Point Of Care And Continuous Blood Glucose Analysis In Critically Ill Icu Patients Critical Care Full Text



Http Www childrens Ca Endocrinology Diabetes Site Documents Glucoseunits Pdf



My Fasting Blood Glucose Is 101 I Googled And Found Out I Am Pre Diabetic But My Doctor Said I Am Not Pre Diabetic Who Is Correct Quora



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿